Introduction
India’s infrastructure is undergoing a revolutionary transformation, and at the heart of it lies one of the most ambitious infrastructure projects in the world: the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC). Envisioned as a high-speed, high-impact economic corridor that will drive industrial growth, create employment opportunities, and urbanize underdeveloped regions, the DMIC stretches across six states and is backed by massive investments and cutting-edge planning.
In this blog, we’ll take a deep dive into every critical element of the DMIC—from its objectives and benefits to its route, cost, status, and how it impacts real estate, logistics, and manufacturing in India.
Also Read:- Samruddhi Mahamarg: Route Map | Distance | Opening Date | News
What is the Objective Behind the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Project?
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor project was conceived to:
- Spur economic growth through industrialization.
- Create new smart cities with state-of-the-art infrastructure.
- Enhance manufacturing capabilities under the Make in India initiative.
- Decongest existing metros by developing new urban hubs.
- Create over 3 million jobs across various sectors.
A joint initiative between the Indian government and the Government of Japan, DMIC has evolved into a flagship project of national importance with international backing.
When Did the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Start?
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor’s start date traces back to 2006, when the Indian and Japanese governments signed a Memorandum of Understanding. The actual planning and ground-level activities began between 2008 and 2011, with various components of the corridor taking shape over the years.
The project was officially launched in phases to allow more structured development, considering its massive scale.
What Does the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Route Cover?

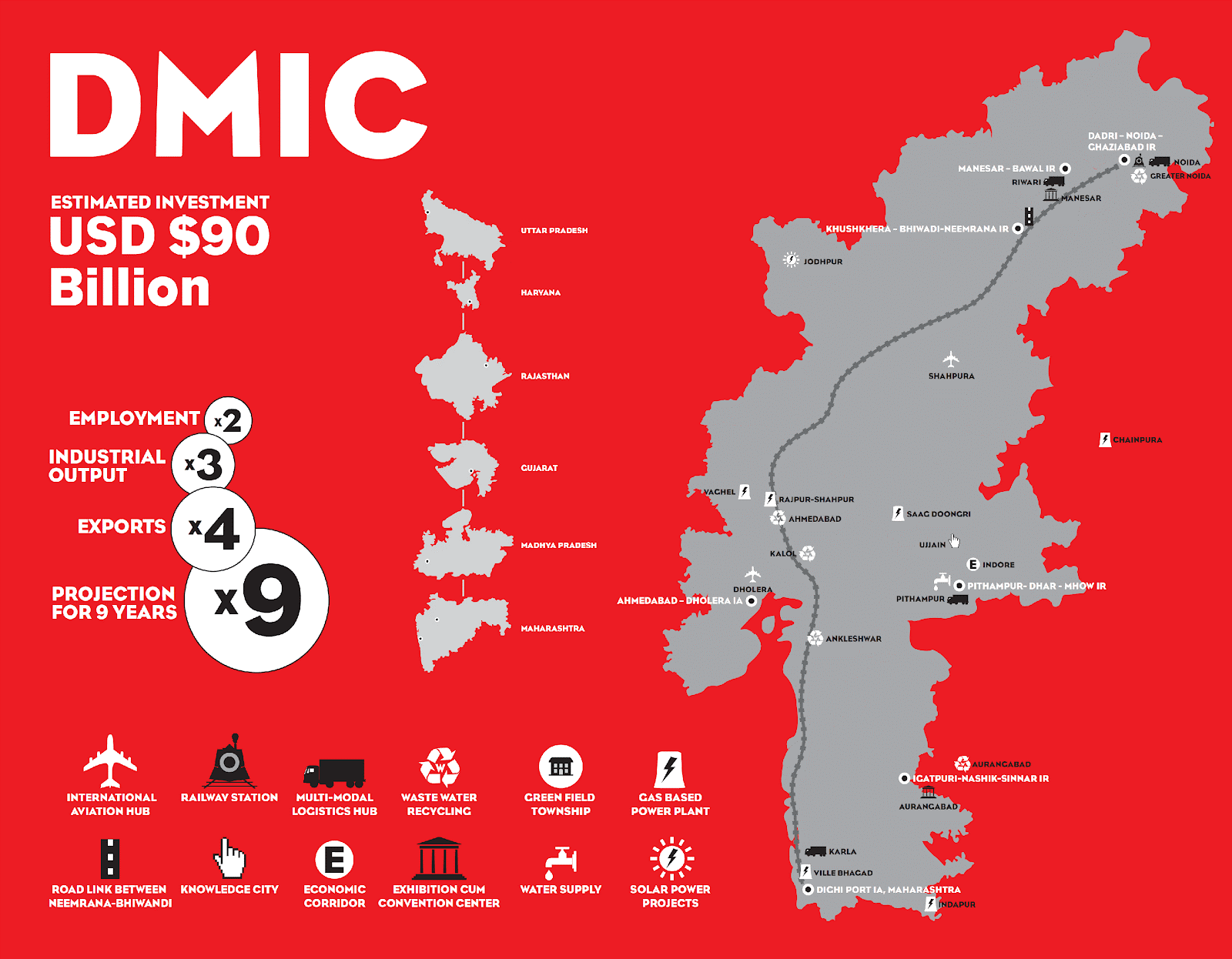
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor route covers approximately 1,500 km, connecting the political capital (Delhi) to the financial capital (Mumbai), traversing through six states:
- Uttar Pradesh
- Haryana
- Rajasthan
- Madhya Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
The backbone of this corridor is the Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC), a high-capacity railway line built exclusively for freight movement. Industrial zones, smart cities, logistics hubs, and manufacturing clusters are being planned along this strategic route.
Also Read:- Ganga Expressway: Route Map | Opening Date | Village List & More
What is the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Map and Its Key Nodes?

The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor map shows 24 investment nodes comprising:
- 13 Industrial Areas
- 8 Smart Cities
- 2 International Airports
- 5 Power Projects
- 2 Mass Rapid Transit Systems
- 2 Logistic Hubs
Prominent nodes include:
- Dholera SIR (Gujarat) – India’s first planned smart city.
- Shendra-Bidkin (Maharashtra) – Integrated Industrial Township.
- Manesar-Bawal (Haryana) – Industrial Model Township.
- Neemrana-Khushkhera (Rajasthan) – Investment Region.
These hubs are designed to be self-sustaining, with residential, commercial, and industrial zones coexisting in harmony.
Also Read:- NH44 National Highway: Route | Map | Distance | News
What is the Current Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Status?
As of 2025, the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor status is marked by partial operationalization and accelerated development of several key nodes.
Operational Highlights:
- Dholera SIR: Roads, underground utilities, and a world-class activation area have been developed.
- Shendra-Bidkin (Maharashtra): Several Japanese firms have set up facilities here.
- Integrated Industrial Township at Greater Noida (Uttar Pradesh): Almost fully developed and attracting global investors.
Further phases are actively under development, with major public and private investments pouring in. However, the progress varies across states and is subject to land acquisition and policy challenges.
What is the Estimated Cost of the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor?

The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor cost is projected to be approximately US$ 90 billion (over INR 8 lakh crore), making it one of the most expensive infrastructure projects in the world.
Key cost components include:
- Western Dedicated Freight Corridor: Approx. INR 81,459 crore.
- Industrial Nodes Development.
- Power, Transport, and Urban Infrastructure.
- Technological platforms for Smart Governance.
The Japanese government, through the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), is funding a significant portion of the project as low-interest loans.
Also Read:- Delhi-Dehradun Expressway: Route | Construction | Map | Status 2025
What is the Expected Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Completion Date?
While the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor completion date was initially set for 2019-2020, the sheer scale and complexity of the project have extended timelines.
As of 2025, the revised timeline estimates complete functional readiness by 2030, with major cities and zones becoming operational by 2026-2027. Key freight and transport components like the WDFC are nearing full completion, which will unlock accelerated growth.
How Will the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Transform Urban India?
DMIC is not just an infrastructure project—it’s a new urban vision. Here’s how:
- Smart Cities: Equipped with IoT-enabled systems for power, water, and traffic.
- Transit-Oriented Development: Promotes pedestrian-friendly cities with integrated metro and freight systems.
- Sustainability: Emphasis on solar energy, green zones, and waste recycling.
- Job Creation: Over 3 million direct and indirect employment opportunities.
- Boost to MSMEs and Startups: Infrastructure and policy incentives to encourage industrial entrepreneurship.
What Are the Challenges Faced by the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor?

Despite its transformative Promise, DMIC has faced several challenges:
- Land Acquisition Delays
- State-Centre Coordination Issues
- Environmental Clearances
- High Project Costs
- Execution Bottlenecks in Tier-2 Cities
However, recent reforms like single-window clearances and easing FDI norms have helped accelerate progress.
Also Read:- Mumbai Trans Harbour Link: Map | Photos | Connectivity – Housiey
How Will Real Estate and Investment Be Impacted by DMIC?
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor is expected to skyrocket real estate demand across its investment regions. Here’s why:
- Residential: Developers are investing in townships near DMIC nodes due to upcoming job hubs.
- Commercial: Warehousing, office parks, logistics, and retail centers are rapidly developing.
- Industrial: MSMEs and MNCs are showing interest in industrial plots and SEZs.
Investing near the DMIC route is likely to offer exponential returns over the next decade, especially in Gujarat, Rajasthan, and parts of Maharashtra.
Conclusion:
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor is a visionary megaproject that can redefine India’s industrial, urban, and economic landscape for generations to come. With smart cities, sustainable planning, seamless logistics, and unparalleled infrastructure, it stands as a testimony to what futuristic India looks like.
For homeowners, real estate investors, startups, and corporates—this is more than an opportunity. It’s a once-in-a-generation transformation.
At Housiey, we closely track developments along the DMIC and help home buyers and investors make informed decisions in emerging micro-markets near the corridor.
If you’re interested in how connectivity infrastructure boosts development, don’t forget to read our blog on the Samruddhi Mahamarg—another path-breaking expressway transforming Maharashtra’s connectivity landscape.
FAQs
Introduction
India’s infrastructure is undergoing a revolutionary transformation, and at the heart of it lies one of the most ambitious infrastructure projects in the world: the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC). Envisioned as a high-speed, high-impact economic corridor that will drive industrial growth, create employment opportunities, and urbanize underdeveloped regions, the DMIC stretches across six states and is backed by massive investments and cutting-edge planning.
In this blog, we’ll take a deep dive into every critical element of the DMIC—from its objectives and benefits to its route, cost, status, and how it impacts real estate, logistics, and manufacturing in India.
Also Read:- Samruddhi Mahamarg: Route Map | Distance | Opening Date | News
What is the Objective Behind the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Project?
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor project was conceived to:
- Spur economic growth through industrialization.
- Create new smart cities with state-of-the-art infrastructure.
- Enhance manufacturing capabilities under the Make in India initiative.
- Decongest existing metros by developing new urban hubs.
- Create over 3 million jobs across various sectors.
A joint initiative between the Indian government and the Government of Japan, DMIC has evolved into a flagship project of national importance with international backing.
When Did the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Start?
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor’s start date traces back to 2006, when the Indian and Japanese governments signed a Memorandum of Understanding. The actual planning and ground-level activities began between 2008 and 2011, with various components of the corridor taking shape over the years.
The project was officially launched in phases to allow more structured development, considering its massive scale.
What Does the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Route Cover?

The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor route covers approximately 1,500 km, connecting the political capital (Delhi) to the financial capital (Mumbai), traversing through six states:
- Uttar Pradesh
- Haryana
- Rajasthan
- Madhya Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
The backbone of this corridor is the Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC), a high-capacity railway line built exclusively for freight movement. Industrial zones, smart cities, logistics hubs, and manufacturing clusters are being planned along this strategic route.
Also Read:- Ganga Expressway: Route Map | Opening Date | Village List & More
What is the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Map and Its Key Nodes?

The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor map shows 24 investment nodes comprising:
- 13 Industrial Areas
- 8 Smart Cities
- 2 International Airports
- 5 Power Projects
- 2 Mass Rapid Transit Systems
- 2 Logistic Hubs
Prominent nodes include:
- Dholera SIR (Gujarat) – India’s first planned smart city.
- Shendra-Bidkin (Maharashtra) – Integrated Industrial Township.
- Manesar-Bawal (Haryana) – Industrial Model Township.
- Neemrana-Khushkhera (Rajasthan) – Investment Region.
These hubs are designed to be self-sustaining, with residential, commercial, and industrial zones coexisting in harmony.
Also Read:- NH44 National Highway: Route | Map | Distance | News
What is the Current Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Status?
As of 2025, the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor status is marked by partial operationalization and accelerated development of several key nodes.
Operational Highlights:
- Dholera SIR: Roads, underground utilities, and a world-class activation area have been developed.
- Shendra-Bidkin (Maharashtra): Several Japanese firms have set up facilities here.
- Integrated Industrial Township at Greater Noida (Uttar Pradesh): Almost fully developed and attracting global investors.
Further phases are actively under development, with major public and private investments pouring in. However, the progress varies across states and is subject to land acquisition and policy challenges.
What is the Estimated Cost of the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor?

The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor cost is projected to be approximately US$ 90 billion (over INR 8 lakh crore), making it one of the most expensive infrastructure projects in the world.
Key cost components include:
- Western Dedicated Freight Corridor: Approx. INR 81,459 crore.
- Industrial Nodes Development.
- Power, Transport, and Urban Infrastructure.
- Technological platforms for Smart Governance.
The Japanese government, through the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), is funding a significant portion of the project as low-interest loans.
Also Read:- Delhi-Dehradun Expressway: Route | Construction | Map | Status 2025
What is the Expected Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Completion Date?
While the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor completion date was initially set for 2019-2020, the sheer scale and complexity of the project have extended timelines.
As of 2025, the revised timeline estimates complete functional readiness by 2030, with major cities and zones becoming operational by 2026-2027. Key freight and transport components like the WDFC are nearing full completion, which will unlock accelerated growth.
How Will the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor Transform Urban India?
DMIC is not just an infrastructure project—it’s a new urban vision. Here’s how:
- Smart Cities: Equipped with IoT-enabled systems for power, water, and traffic.
- Transit-Oriented Development: Promotes pedestrian-friendly cities with integrated metro and freight systems.
- Sustainability: Emphasis on solar energy, green zones, and waste recycling.
- Job Creation: Over 3 million direct and indirect employment opportunities.
- Boost to MSMEs and Startups: Infrastructure and policy incentives to encourage industrial entrepreneurship.
What Are the Challenges Faced by the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor?

Despite its transformative Promise, DMIC has faced several challenges:
- Land Acquisition Delays
- State-Centre Coordination Issues
- Environmental Clearances
- High Project Costs
- Execution Bottlenecks in Tier-2 Cities
However, recent reforms like single-window clearances and easing FDI norms have helped accelerate progress.
Also Read:- Mumbai Trans Harbour Link: Map | Photos | Connectivity – Housiey
How Will Real Estate and Investment Be Impacted by DMIC?
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor is expected to skyrocket real estate demand across its investment regions. Here’s why:
- Residential: Developers are investing in townships near DMIC nodes due to upcoming job hubs.
- Commercial: Warehousing, office parks, logistics, and retail centers are rapidly developing.
- Industrial: MSMEs and MNCs are showing interest in industrial plots and SEZs.
Investing near the DMIC route is likely to offer exponential returns over the next decade, especially in Gujarat, Rajasthan, and parts of Maharashtra.
Conclusion:
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor is a visionary megaproject that can redefine India’s industrial, urban, and economic landscape for generations to come. With smart cities, sustainable planning, seamless logistics, and unparalleled infrastructure, it stands as a testimony to what futuristic India looks like.
For homeowners, real estate investors, startups, and corporates—this is more than an opportunity. It’s a once-in-a-generation transformation.
At Housiey, we closely track developments along the DMIC and help home buyers and investors make informed decisions in emerging micro-markets near the corridor.
If you’re interested in how connectivity infrastructure boosts development, don’t forget to read our blog on the Samruddhi Mahamarg—another path-breaking expressway transforming Maharashtra’s connectivity landscape.
FAQs